Note
Click here to download the full example code
cluster generation¶
This example demonstrates how to perform highly variable gene selection, PCA, nearest neighbor calculation, and clustering.
import besca as bc
import scanpy as sc
import pytest
# pytest.skip('Test is only for here as example and should not be executed')
# import example dataset that has previously been filtered
adata = bc.datasets.pbmc3k_filtered()
## We get the raw matrix containing all the initial genes, keeping the filtering on the cells
adata = bc.get_raw(adata)
highly variable gene selection¶
select highly variable genes (considers correction for gene expression level)
# define thresholds for highly variable genes
variable_genes_min_mean = 0.01
variable_genes_max_mean = 5
variable_genes_min_disp = 0.4
# identify genes with variable expression
filter_result = sc.pp.filter_genes_dispersion(
adata.X,
min_mean=variable_genes_min_mean,
max_mean=variable_genes_max_mean,
min_disp=variable_genes_min_disp,
)
sc.pl.filter_genes_dispersion(filter_result)
nbr_variable_genes = sum(filter_result.gene_subset)
print("number of variable genes selected ", nbr_variable_genes)
# perform the actual filtering
adata = adata[:, filter_result.gene_subset]
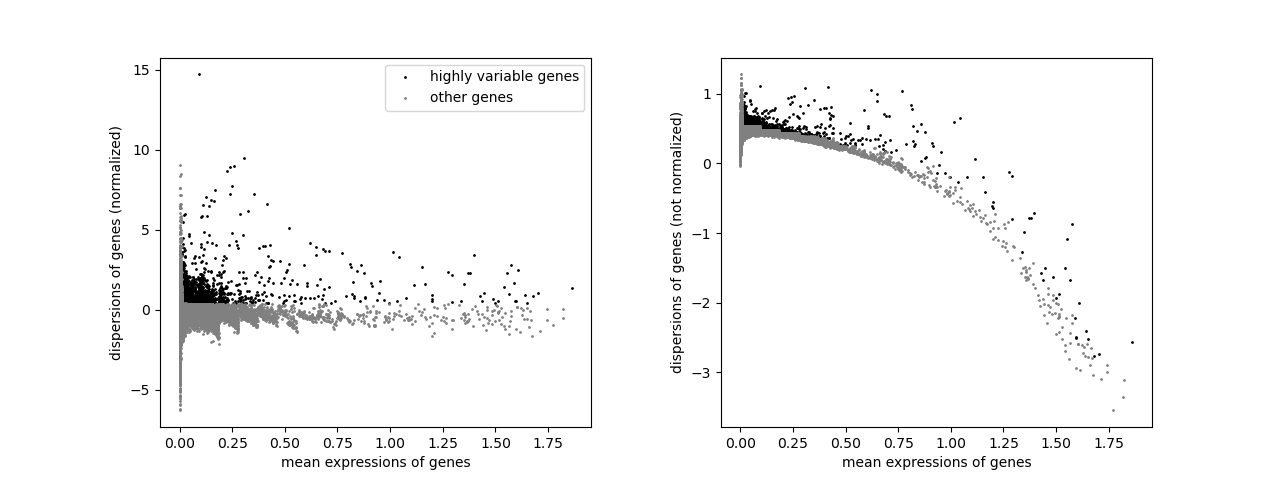
number of variable genes selected 1897
set random seed¶
To get reproducible results you need to define a random seed for all of the stochastic processes, such as e.g. PCA, neighbors, etc.
# set random seed
random_seed = 0
PCA¶
# log transform our data (is easier to work with numbers like this)
sc.pp.log1p(adata)
# Scale data to unit variance and zero mean, and cut-off at max value 10
sc.pp.scale(adata, max_value=10)
# calculate 50 principle components of the dataset
sc.tl.pca(adata, random_state=random_seed, svd_solver="arpack")
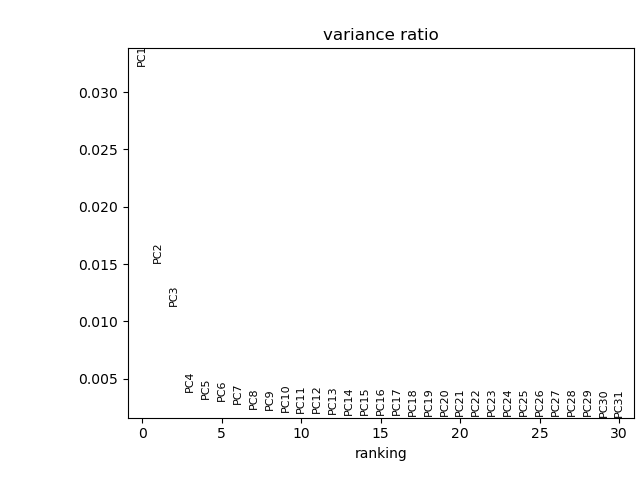
# visualize the amount of variance explained by each PC
sc.pl.pca_variance_ratio(adata)
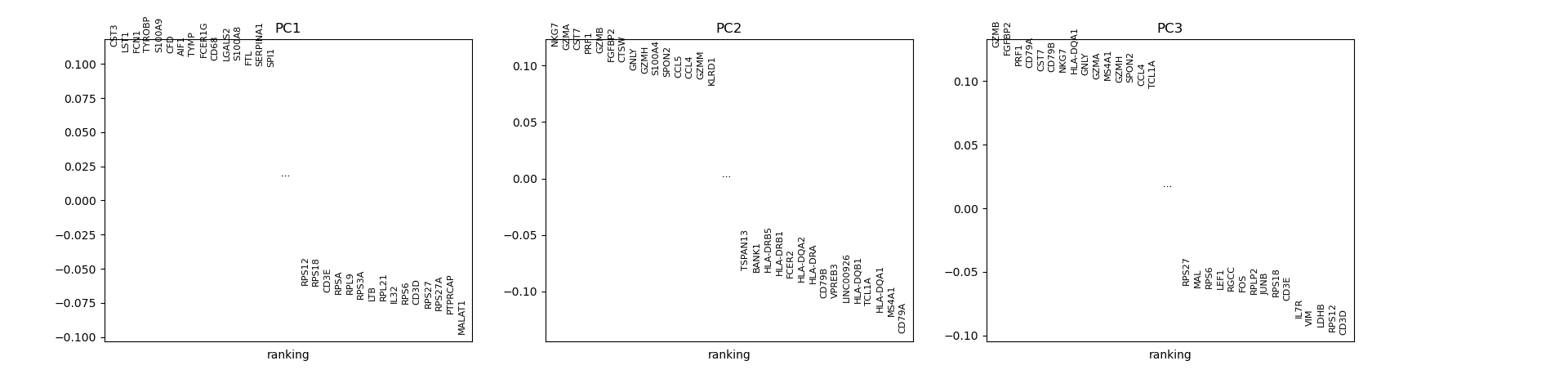
# visualize the loadings onto the first 3 PCs
sc.pl.pca_loadings(adata)
nearest neighbors¶
sc.pp.neighbors(adata, n_neighbors=15, random_state=random_seed, n_pcs=50)
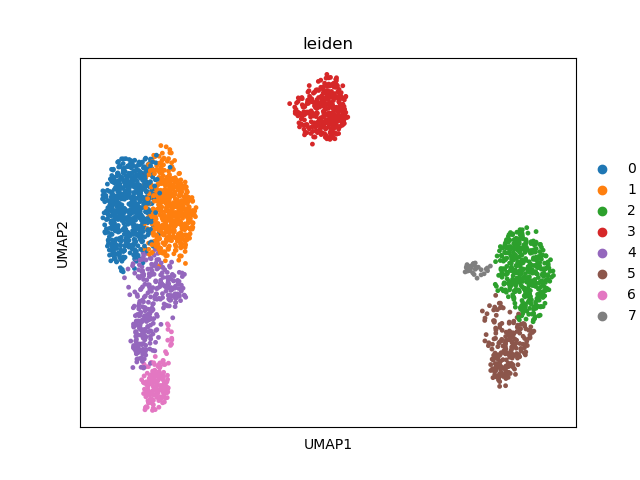
leiden clustering¶
sc.tl.leiden(adata, random_state=random_seed)
UMAP and t-SNE generation¶
# calculate UMAP
sc.tl.umap(adata, random_state=random_seed)
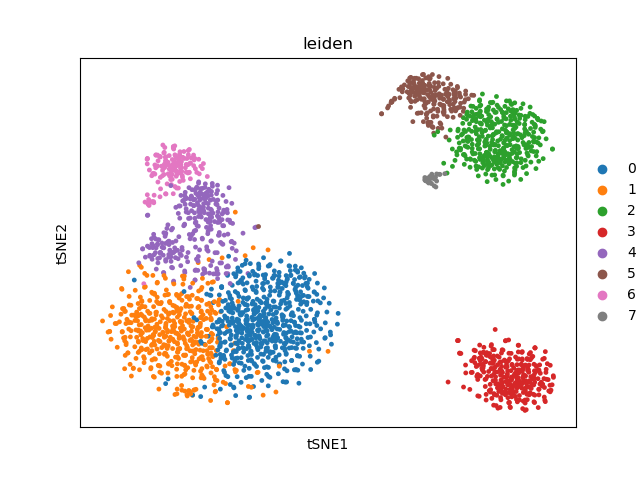
# calculate t-SNE
sc.tl.tsne(adata, random_state=random_seed)
visualize the results¶
sc.pl.umap(adata, color=["leiden"])
sc.pl.tsne(adata, color=["leiden"])
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 11.037 seconds)